Forensic Audit
Forensic audit is used to uncover criminal behaviour such as fraud or embezzlement.During forensic audit ,we seek to derive evidence that could be potentially be used in court
How forensic Audit Works
Forensic audit involves planning the investigation,collecting evidence and writting a report
Planning and investigation
Auditors plan their investigations to achieve the following objectives
- Identifying which fraud
- The period the fraud occured
- How the fraud was concealed
- Identifying masterminds
- Quantifying loss suffered as a result
- Gathering evidence thatcan be used in court
- Suggestions on how to seal such loopholes
Collecting evidence
Evidence gathered should be sufficient to prove in a court the details of the fraud ,loss suffered and affected parties
Reporting
At the end of the forensic audit a report is documented to be used to file legal proceedings should they choose so.Also the report should include suggestions on how to prevent such frauds in the future
Financial statement fraud
For many reasons a company directors may prepare financial statements fraudilently.This reasons could be to attract investors,evade paying taxes,to receive bonuses,to meet forcusted targets etc
Forensic Account
Forensic accounting uses investigating skills to conduct an examination into the finances of a business or an individual

Asset misappropriation
Asset misappropriation is the most common form of fraud..Asset misappropriation coulb be in the form of stealing cash,forging invoices,paying ghost suppliers etc
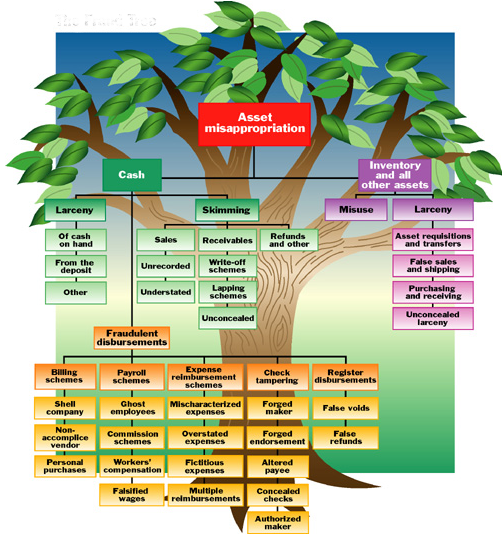
misappropriation tree
Fraud Triangle Theory

According to Albrecht, the fraud triangle states that “individuals are motivated to commit fraud when three elements come together: (1) some kind of perceived pressure, (2) some perceived opportunity, and (3) some way to rationalize the fraud as not being inconsistent with one's values.”
Fraud is an intentional deception by an employee or an organization for personal gain.The underlying reasons why fraud is commited can be narrowed down to rationale ,incentive expectations and opportunity available.
Today, the fraud triangle is widely used by anti-fraud professionals to explain conditions that could motivate individuals or companies to engage in fraud. The model can also be used to highlight economic or industry-wide conditions that can lead to a higher overall risk. To identify risk, anti-fraud professionals look for the presence of the following three factors:
- Motivation
- Opportunity
- Rationalization
